UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH ON THE MOLECULAR GENETICS OF ANIMAL DEVELOPMENT
Laboratory of Bruce Wightman, Biology DepartmentNew Science Building 221Our laboratory is studying the mechanisms of animal development, using the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans as a model system. We perform experiments that include Mendelian genetic, molecular genetic, genomic, and biochemical approaches. Research students in our lab learn valuable technologies, help design experiments, interpret data, publish papers and attend scientific conferences. The Wightman Lab has received federal grant support from the National Science Foundation and National Institutes of Health.The nuclear hormone receptors are a class of evolutionarily-conserved proteins that regulate transcription of other genes in all known animals, from coral to humans. In a variety of species, nuclear hormone receptors play critical roles in physiology and development. For example, the androgen receptors mediate male sex development, estrogen receptors function in female physiology, and ecdysone receptors control insect morphogenesis. Many, but not all, nuclear receptors are activated in response to small lipophilic hormones, such as estrogen. The small soil-dwelling roundworm C. elegans, like other nematodes, has seen an explosion in the number and variety of nuclear receptors. While humans have only 48 nuclear receptors, C. elegans has over 270. Our lab is focused on the NR2E class of nuclear receptors. In vertebrates, two genes of this class have been studied: PNR (NR2E3), which functions in the development of rod and cone photoreceptor neurons in human retina, and tailless, which functions in the development of adult neural stem cells and limbic system in mice. We are studying the C. elegans versions of these genes: fax-1 (PNR), nhr-67 (tailless), nhr-111 (worm-specific), and nhr-239 (found in most animals except vertebrates). Each nuclear receptor has two important parts (domains) in the protein: the DNA-binding domain (DBD), which is the part that binds to DNA in the promoter of other genes, and the ligand-binding domain (LBD), which is the part that binds a hormone (if there is one) and mediates changes in the rate of transcription of genes that a regulated by the nuclear receptor. In contrast to the DBD, where amino acid sequence is very similar in worms, flies and humans, the sequence of the LBD is very different in worms as compared to other species. Furthermore, our lab showed that the LBD is not required for some functions, suggesting that C. elegans nuclear receptors may sometimes be ligand-independent.Picture of nematode:
Nuclear receptors regulate transcription of other genes by binding to promoter DNA
sequences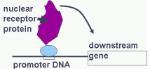
CURRENT RESEARCH PROJECTS
Function of fax-1 in neuronal control of developmental progression and sleep
The FAX-1 nuclear receptor of C. elegans functions in neuron identity and is orthologous to vertebrate PNR nuclear receptor (NR2E3). In humans, mutations in PNR lead to defects in photoreceptor development and subsequent retinal degeneration. fax-1 mutants exhibit a slow growth phenotype, which is a result of a defect in execution of the L1 transition. Newly hatched C. elegans larvae (L1s) make a developmental decision to either initiate growth or arrest development, based on whether or not food is available. Arrested L1 animals then resume growth once in the presence of food. fax-1 mutants undergo a temporary L1 arrest when hatching in the presence of food, likely a consequence of fax-1 function in the nervous system. Combining fax-1 or unc-42 (a different type of transcription factor) mutations with a mutation in daf-2 insulin receptor causes all animals to arrest just before hatching or as newly-hatched L1 animals. These animals are asleep! Mutations in a gene required for sleep can reverse the arrest. This has led us to propose the existence of a wake-promoting neural pathway that is involved in insulin-signaling and depends on fax-1 and unc-42- expressing neurons. |
THE WIGHTMAN LABORATORY
PERSONNEL
Bruce Wightman, lab head
Erin Jackson ('25)
Ashley Kim ('25)
Jocelyn Mertz ('25)
Benjamin Mulford ('26)
Pamela Najm ('27)
Alyssa Sipman ('26)
Sydney Vogel ('25)
LAB ALUMNI
Alumni of the Wightman lab have gone on to pursue graduate and professional study at institutions such as Stanford University, Columbia University, Cornell University, University of Pennsylvania, and Yale University. They have won competitive awards such as the NSF Graduate Fellowship, British Marshall Scholarship, and Fulbright Scholarship.
|
Vivi Arking ('25) Long Nguyen ('23) Genna Albert '03 Emily Brennan ('09) Michelle Seif '06 Sheila Clever, former technician |
|
RECENT PUBLICATIONS AND PRESENTATIONS
Bayer, EA (’14), Liberatore, KM (’19), Evan Schlesinger, E (’20), Schneider JR (’21), He Z. (’19), Birnbaum, S (’18), and Wightman, B, 2022, Insulin-like peptide signaling promotes arousal and developmental progression in C. elegans, Genetics, 220(1): iyab202. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab202. PMID: 34788806; PMCID: PMC8733457..
Mardick JI, Rasmussen NR, Wightman B, Reiner DJ, 2021, Rap1>RalGEF>Ral and Ras signals sculpt the C. elegans nervous system, Developmental Biology, 477: 37-48.
Suresh, A. (’19) and Wightman, B., 2020, The daf-2 insulin receptor functions in C. elegans embryo elongation. microPublication Biology. https://doi.org/10.17912/micropub.biology.000117
Bodofsky, S. (’18), Liberatore, K. (’19), Pioppo, L. (’12), Lapadula, D. (’14), Thompson, L. (’18), Birnbaum, S. (’18), McClung, G. (’12), Kartik, A. (’17), Clever, S. and Wightman, B., 2018, A tissue-specific enhancer of the C. elegansnhr-67/tailless gene drives coordinated expression in uterine stem cells and the differentiated anchor cell, Gene Expr Patterns, 30: 71-81, doi: 10.1016/j.gep.2018.10.003. PubMed PMID: 30404043.
Bodofsky, S. ('18), Koitz, F. ('19), and Wightman, B., 2017, Conserved and Exapted Functions of Nuclear Receptors in Animal Development, Nuclear Receptor Research, 4: 1-34, Article ID 101305.
K. Liberatore (’19) and B. Wightman, 2018, Insulin signaling and neuronal function in arousal in C. elegans, 21st Undergraduate Research Symposium, U. Maryland, Baltimore Co., Baltimore, MD, October 20. Regional Conference. *Second Place Award in Poster Competition*
Z. He (’19) and B. Wightman, 2018, The role of insulin signaling and neuron function in developmental progression, 21st Undergraduate Research Symposium, U. Maryland, Baltimore Co., Baltimore, MD, October 20. Regional Conference.
F. Koitz (’19) and B. Wightman, 2018, The C. elegans RevErb gene, nhr-85, is expressed increasingly over the first half of larval development, 21st Undergraduate Research Symposium, U. Maryland, Baltimore Co., Baltimore, MD, October 20. Regional Conference.
S. Bodofsky (’18), K. Liberatore (’19), and B. Wightman, 2018, Conserved cis-acting elements in the nhr-67 promoter mediate organogenesis in C. elegans, Lehigh Valley Molecular and Cell Biology Symposium, DeSales University, April 24. Regional Conference.
F. Koitz (’19) and B. Wightman, 2018, Function of the nhr-85/RevErb gene in C. elegans, Lehigh Valley Molecular and Cell Biology Symposium, DeSales University, April 24. Regional Conference.
S. Birnbaum (’18) and B. Wightman, 2018, Neural regulation of sleep-like state by the gene fax‑1 in the nematode C. elegans, Lehigh Valley Molecular and Cell Biology Symposium, DeSales University, April 24. Regional Conference.
D. Silver (’18), S. Clever and B. Wightman, 2018, Sleep and Insulin Signaling Pathway in C. elegans, Lehigh Valley Molecular and Cell Biology Symposium, DeSales University, April 24. Regional Conference.
L. Thompson (’18) and B. Wightman, 2018, Understanding NHR-67 regulation of genes involved in C. elegans ventral uterine development, Lehigh Valley Molecular and Cell Biology Symposium, DeSales University, April 24. Regional Conference.
B. Wightman, 2018, Insulin-dependent quiescence and arrest at hatching, C. elegans Developmental Biology and Gene expression Meeting, Barcelona, Spain, June 13-17. International Conference.
B. Wightman, K. Lightfoot (’17) and E. Bayer (’14), 2017, The fax-1 and nhr-85 nuclear receptors of C. elegans function in gonad development, 21st International C. elegans Conferences, UCLA, Los Angeles, June 21-25.
S. Bodofsky (’18), S. Birnbaum (’18), L. Thompson (’18), S. Clever and B. Wightman, 2017, An nhr-67 promoter element mediates expression in AC and VU uterine cells, 21st International C. elegans Conferences, UCLA, Los Angeles, June 21-25.
F. Koitz (’19), E. Bayer (’14), S. Clever and B. Wightman, 2017, FAX-1 and UNC-42 transcription factors mediate insulin-dependent quiescence and arrest, 21st International C. elegans Conferences, UCLA, Los Angeles, June 21-25.
C. Berman (’16), Akshara Kartik (’17), S. Clever, B. Wightman, 2016, A promoter element in the C. elegans nhr-67 tailless gene mediates hlh-2/daughterless regulation of anchor cell differentiation and uterine organogenesis, The Allied Genetics Conference, Orlando, FL, July 13-17. International Conference.
S. Saltzman (’16), E. Bayer (’14), S. Clever, B. Wightman, 2016, The fax-1 nuclear receptor of C. elegans functions in gonad development, The Allied Genetics Conference, Orlando, FL, July 13-17. International Conference.
B. Wightman, E. Bayer (’14), S. Clever, 2016, FAX-1 and UNC-42 Transcription Factors Regulate Developmental Arrest in C. elegans, The Allied Genetics Conference, Orlando, FL, July 13-17. International Conference.
S. Bodofksy (’18), S. Clever, B. Wightman, 2016, A promoter element in the C. elegans nhr-67 tailless gene mediates regulation of cell differentiation and uterine organogenesis, Lehigh Valley Molecular and Cell Biology Symposium, DeSales University, April 21. Regional Conference.
S. Birnbuam (’18), S. Clever, B. Wightman, 2016, The conserved nuclear receptor fax-1 functions in neuronal regulation of lifecycle progression in C. elegans, Lehigh Valley Molecular and Cell Biology Symposium, DeSales University, April 21. Regional Conference.
B. Wightman, 2016, Regulation of developmental arrest in C. elegans by transcription factors that specify neuron identity, invited lecture, Rowan University School of Osteopathic Medicine, Stratford, NJ, March 10.
B. Wightman, E. Bayer (’14), L. Jerjos (’17), C. Greco (’15), M. Kramer (’15), M. Kho (’15), K. Skwirut (’16), A. Kartik (’17), S. Clever, 2015, The FAX-1 and NHR-67 Nuclear Receptors Function in Gonad Development, presentation (BW) at the 20th International C. elegans Meeting, Los Angeles, CA, June 24-28. International Conference.
C. Greco, A. Kartik, S. Clever, B. Wightman, 2015, A promoter element in the C. elegansnhr-67 tailless gene mediates hlh-2/daughterless regulation of uterine organogenesis, presentation (CG and AK) at the 2015 Mid-Atlantic Society for Developmental Biology Meeting, Princeton, NJ, March 27-28. Regional Conference.
D. Lapadula, P. Ezzio, L. Pioppo, M. Kho, P. Schartel, Z. Shuler, C. Greco, M. Kramer, S. Clever, B. Wightman, 2014, a promoter element in the C. elegans tailless gene links sex-specific regulation with uterine organogenesis, presentation (DL) at the 2014 Mid-Atlantic Society for Developmental Biology Meeting, Baltimore MD, May 30-31.
E. Bayer, B. Wightman, 2014, the conserved nuclear receptor fax-1 functions in C. elegans cell migration and neuronal regulation of lifecycle, presentation (EB) at the 2014 Mid-Atlantic Society for Developmental Biology Meeting, Baltimore MD, May 30-31.
E. Bayer, B. Wightman, 2013, Function of the conserved nuclear receptor fax-1 in C. elegans cell migration and sleep regulation presentation (EB) at the 16th Undergraduate Research Symposium, U. Maryland, Baltimore Co., Baltimore, MD, Oct. 26. Regional Conference. *First Place Award in Poster Competition*
D. Lapadula, P. Ezzio, S. Clever and B. Wightman, 2013, A promoter element in the C. elegans tailless gene links sex-specific regulation with uterine organogenesis, presentation (DL) at the 16th Undergraduate Research Symposium, U. Maryland, Baltimore Co., Baltimore, MD, Oct. 26. Regional Conference. *First Place Award in Poster Competition*
E. Bayer and B. Wightman, 2013, fax-1 and prominin function in migration and morphogenesis, presentation (BW) at the 19th International C. elegans Meeting, Los Angeles, CA, June 26-30. International Conference.



